 What is tendonitis?
What is tendonitis?- What causes tendonitis?
- What are the symptoms of tendonitis?
- How do doctors treat tendonitis?
- Where should I go to treat my tendonitis?
Sports injuries can be devastating, especially for those who depend on exercise as part of their daily routines. When these injuries occur, we are reminded just how much we rely on our bodies—from walking to running, swimming to lifting weights, our muscles, tendons, and joints can take a lot of abuse, absorbing the impact of our physical activity. If something goes wrong, we’re often at a loss for what to do.
When these injuries occur, our first instinct can be to push through the pain until it goes away. However, this approach seldom works, leading to worsening symptoms and decreased mobility. In fact, leaving sports injuries untreated for longer can increase the length of recovery times, delaying your return to normal activities.
Tendonitis is a common sports injury but can be caused by other forms of physical activity. It often results from the repetitive use of certain muscle groups, which puts stress on the connective tissues and tendons around the joint. The condition is also not isolated to a specific area of your body—whether it’s your shoulder or ankle, tendonitis can affect anywhere that muscle connects to bone.
But what is tendonitis? How do doctors treat it?
In this article, we’ll break down what tendonitis is, what causes it, and what you can do to relieve your worst symptoms to get back to doing what you love.
What Is Tendonitis?
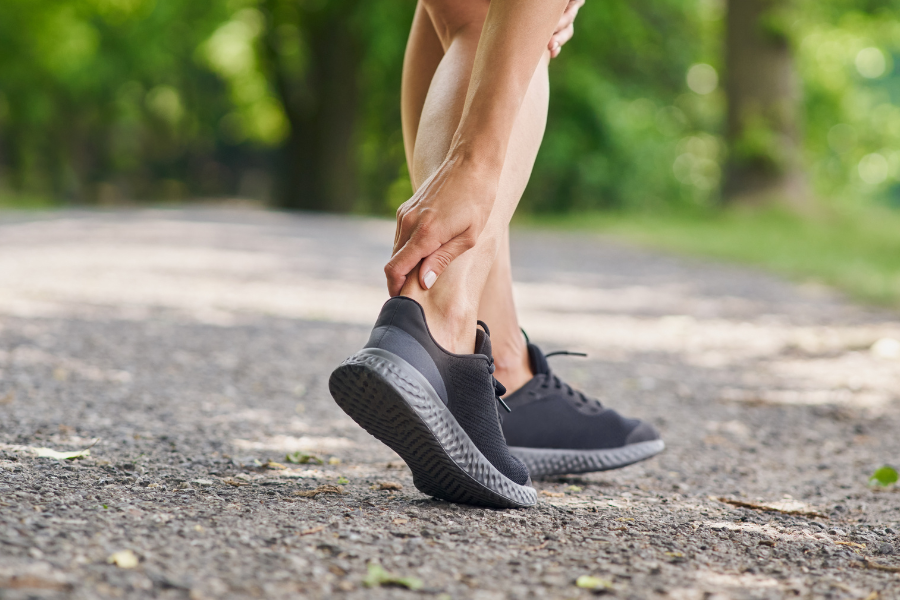
 Tendonitis refers to the inflammation or degeneration of tissue around muscles and bones. The condition occurs when a tendon—the thick fibrous cord that attaches muscles to bones—becomes inflamed or irritated.
Tendonitis refers to the inflammation or degeneration of tissue around muscles and bones. The condition occurs when a tendon—the thick fibrous cord that attaches muscles to bones—becomes inflamed or irritated.
Tendonitis usually occurs as a result of repetitive movements or overuse of a particular tendon, leading to micro-tears in the tendon tissue and subsequent inflammation.
These tears can be painful, restricting mobility. With continued use of the damaged tendon, the pain can worsen and spread, causing debilitating symptoms that prevent your participation in normal activities.
Although tendonitis is a short-term condition, leaving the issue untreated can cause it to recur or become chronic.
What Causes Tendonitis?
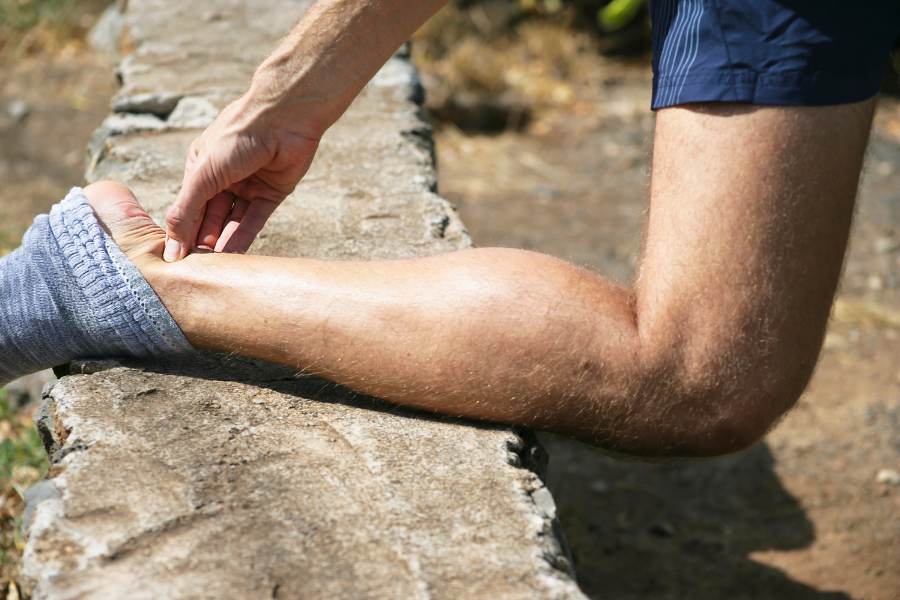
 In most cases, tendonitis results from repeated, minor injuries to the tendon, which can also be described as repetitive stress or overuse.
In most cases, tendonitis results from repeated, minor injuries to the tendon, which can also be described as repetitive stress or overuse.
While athletics are often cited as a principal cause of the condition, patients can develop tendonitis from a wide range of activities, including:
- Sports
- Running/Jogging
- Weightlifting
- Typing
- Bad Posture
- Poor Arch Support
- Manual Labor
- And More
While these are only a few examples, any activity that requires repetitive movements or sitting in an awkward position for long periods can result in damage to your tendons.
The condition may develop suddenly in response to a specific movement—however, in many cases, tendonitis will develop gradually over time, worsening progressively with use.
Another important factor is a patient’s age. The older we get, the less our bodies can adjust and recover from strenuous physical activity, increasing the likelihood of tendonitis in patients over a certain age.
What Are the Symptoms of Tendonitis?
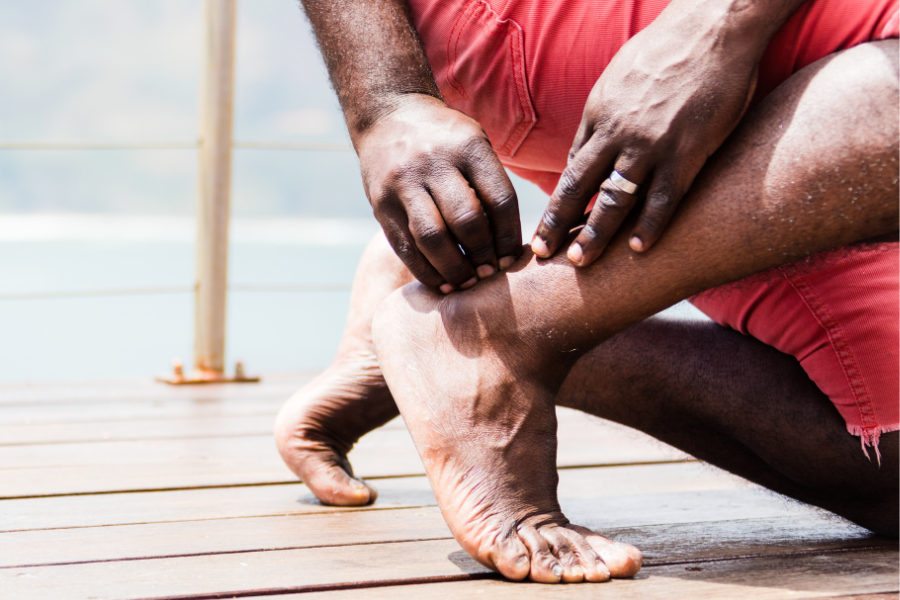 The symptoms of tendonitis can vary from person to person and can range in intensity depending on the affected area and the extent of the injury.
The symptoms of tendonitis can vary from person to person and can range in intensity depending on the affected area and the extent of the injury.
Common symptoms of tendonitis include:
- Pain
- Difficulty Moving
- Swelling
- Warmth/Redness
- “Cracking” Sensation (when moving the affected area)
Depending on the severity of your injury, your doctor will diagnose your condition by conducting a thorough physical examination of the area. If your chronic pain persists, doctors may also request imaging tests such as X-rays, an MRI, ultrasound scans, and blood testing.
Once properly diagnosed, your doctor will develop a personalized treatment plan to target the damaged tissues and encourage healing in the tender areas.
How Do Doctors Treat Tendonitis?
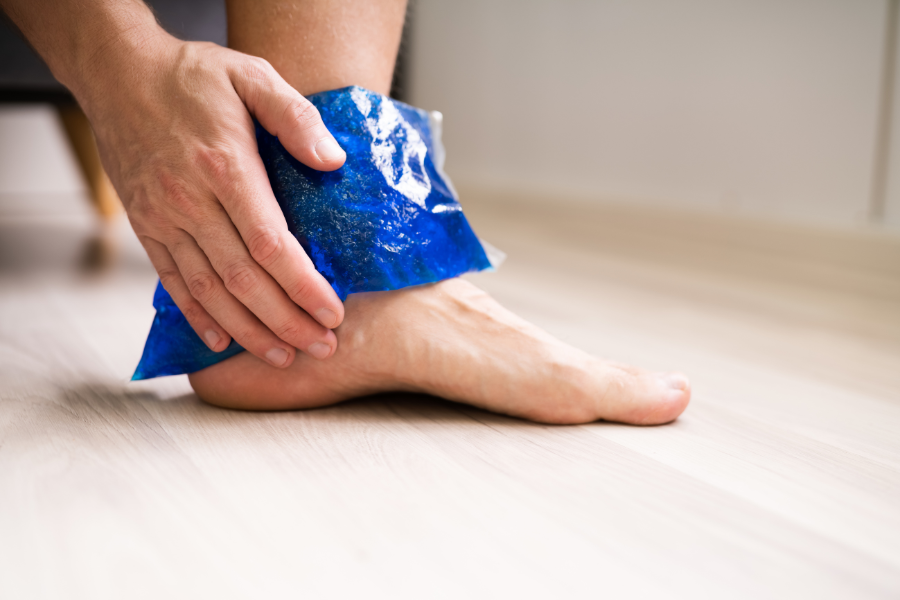 Treatment can vary depending on the cause and severity of your injury. For patients where tendonitis occurs at work or is related to workplace injury, your healthcare provider may suggest worksite intervention.
Treatment can vary depending on the cause and severity of your injury. For patients where tendonitis occurs at work or is related to workplace injury, your healthcare provider may suggest worksite intervention.
However, for most patients, common treatment approaches include:
- Rest (avoid performing the activity that caused the injury to prevent damage from worsening)
- Ice (a cold compress on the affected area for 10-15 minutes once or twice a day can reduce both pain and inflammation)
- Medication (for persistent, NSAIDs such as aspirin, ibuprofen, or naproxen will also help to reduce inflammation and pain)
In rare cases, doctors may also recommend corticosteroid injections if the pain does not subside with NSAIDs. Patients with severe pain may also use supports such as a cane and/or custom-made braces to keep weight off the damaged tendon and its surrounding muscle groups.
For chronic tendonitis, physical therapy and regular exercises can help maintain the strength and function of the muscle, while relieving the symptoms of overuse and stress.
In severe cases, when the tendon itself has ruptured, surgery may be a helpful treatment strategy to lessen pain.
Who Should I Go to for Tendonitis?
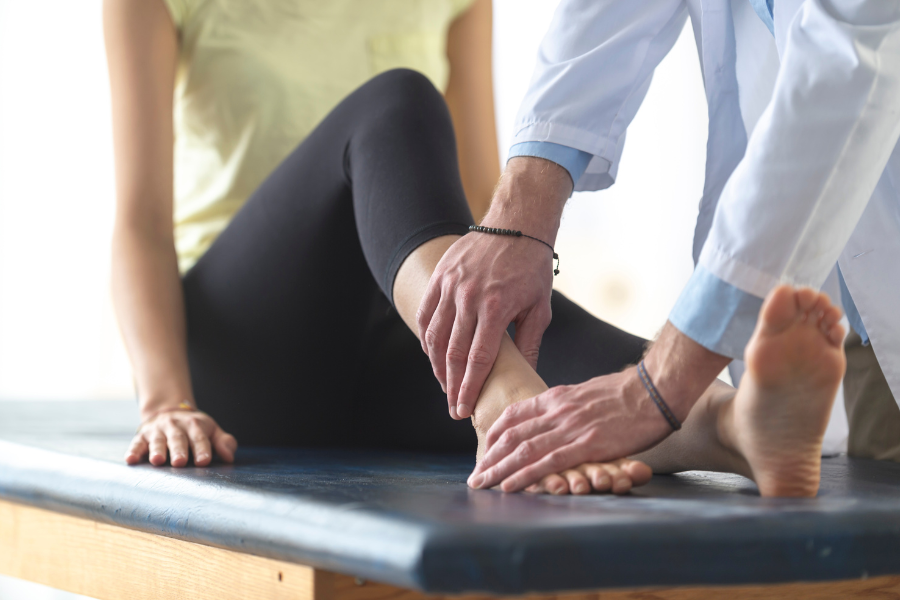 Getting a diagnosis is the first step toward receiving the treatment that can help you recover from your injury. Many patients with tendonitis incorrectly assume that their pain is caused by bruising or simple muscle strain.
Getting a diagnosis is the first step toward receiving the treatment that can help you recover from your injury. Many patients with tendonitis incorrectly assume that their pain is caused by bruising or simple muscle strain.
Seeing a doctor can help clarify the source of your issue, preventing it from becoming a chronic condition while relieving your symptoms before they develop into a serious concern.
At Celebration Foot & Ankle Institute, our team of specialists has years of experience diagnosing and treating foot and ankle conditions, helping patients with tendonitis overcome their condition with personalized treatments and therapies that target their symptoms at the source.
Our doctors understand just how important your physical health is to your well-being. With our support, we can help you recover, heal, and return to doing what you love.


